Install WordPress on Ubuntu 22.04
Traducciones al EspañolEstamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.
WordPress is one of the most common content management systems (CMS) in use today. WordPress allows Ubuntu and other Linux users to design a website and add content using its intuitive GUI. WordPress also allows site owners to install a diverse selection of themes and plug-ins to further customize their site. This guide explains how to install WordPress on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS. It also describes how to configure and start using WordPress after installation.
What is WordPress?
WordPress is a long-time foundation for personal websites and blogs. It is available for free and considered easy to install, configure, and use. It allows site owners to design an attractive site and add information without knowing anything about HTML or CSS. It also features additional modules for further customization along with a large, knowledgeable, and passionate user base. WordPress is available for all major operating systems, although it is most commonly used with Linux.
WordPress can be downloaded to an Ubuntu server using wget. It only requires minor pre-installation configuration changes to other applications. However WordPress relies on several other applications to function. It uses the PHP programming language, so PHP must already be installed. In addition, WordPress requires a web server and a relational database management system (RDBMS).
WordPress Prerequisites
A Ubuntu LAMP or LEMP stack satisfies all these prerequisites. A LAMP stack includes the Linux operating system, the Apache web server, the MySQL RDBMS, and the PHP programming language. A LEMP stack substitutes NGINX (pronounced “engine-x”) in place of Apache and sometimes uses the MariaDB database instead of MySQL. Either stack can be installed using the standard Ubuntu library. For information on installing a LAMP stack on Ubuntu 22.04, see the Linode guide. There is also a Linode guide to installing a LEMP stack on Ubuntu 22.04.
For greater security, WordPress highly recommends HTTPS. However, these instructions work whether HTTPS is configured on the server or not. For information about enabling HTTPS on Ubuntu, see the Linode guide on enabling HTTPS on Apache. An alternate guide for NGINX is also available.
Before You Begin
If you have not already done so, create a Linode account and Compute Instance. See our Getting Started with Linode and Creating a Compute Instance guides.
Follow our Setting Up and Securing a Compute Instance guide to update your system. You may also wish to set the timezone, configure your hostname, create a limited user account, and harden SSH access.
Fully configure a LAMP or LEMP stack on the Linode and confirm it is working properly.
sudo. If you are not familiar with the sudo command, see the
Users and Groups guide.How to Prepare the LAMP or LEMP Stack for WordPress
To properly configure and use WordPress on Ubuntu, a LAMP or LEMP stack must already be installed and working. However, WordPress requires a few additional modifications to the various LAMP/LEMP Stack components. In the following examples, replace example.com with the actual domain name wherever it appears.
How to Configure Apache for WordPress
If you are using a LAMP stack, enable an additional Apache module and restart the server. Follow these steps to configure Apache to support WordPress.
Enable the rewrite module. This allows for more readable links within the site.
sudo a2enmod rewriteEnabling module rewrite.(Optional) To allow WordPress plug-ins and extensions to use
.htaccessfiles, set theAllowOverridedirective to enable them. Add the following configuration to theVirtualHostblock within the site configuration file. This file is normally located at/etc/apache2/sites-available/example.com.conf. For theDirectoryname, use the actual domain name instead ofexample.com.Note If you are not using a site configuration file, skip this step.- File: /etc/apache2/sites-available/example.com.conf
1 2 3 4 5 6 7<VirtualHost *:80> ... <Directory /var/www/html/your_domain/public_html/> AllowOverride All </Directory> ... </VirtualHost>
Run the Apache
configtestutility to test the changes. It might display some warnings, but ifSyntax OKappears in the output, the syntax is valid.sudo apache2ctl configtestSyntax OKRestart Apache.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
How to Configure NGINX for WordPress
If you are using a LEMP stack, make the following configuration changes.
Edit the site configuration file at
/etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com. Make the following change to thelocation /block. Addindex.phpto the start of theindexfield. This tells NGINX to search for this file first.- File: /etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com.conf
1 2 3 4 5 6... location / { index index.php index.html index.htm; try_files $uri $uri/ =404; } ...
Use
unlinkto disable the default NGINX configuration file.sudo unlink /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/defaultRestart NGINX to reload the configuration.
sudo systemctl restart nginx
How to Configure MySQL for WordPress
WordPress uses a separate SQL database to store the site’s contents and configuration. Use the following commands to create a database and a database user. These steps apply to both MySQL and MariaDB.
Log in to MySQL as
root.sudo mysql -u rootNote If you followed all the instructions in our prerequisite guide for LAMP, usesudo mysql -u root -pinstead, and enter your password when prompted.Create a database named
wordpress.CREATE DATABASE wordpress;Create a new user for the
wordpressdatabase and grant the user all rights. Flush all privileges at the end. In the following commands, replacewpuserwith a unique user name andpasswordwith a more secure password.CREATE USER 'wpuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON wordpress.* TO 'wpuser'@'localhost'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Exit the database.
exit
How to Configure PHP for WordPress
Although WordPress can be installed using the default PHP packages, many plug-ins and themes require additional modules. Follow these instructions to upgrade PHP.
For greater flexibility, install the following PHP components.
sudo apt install php-curl php-gd php-mbstring php-xml php-xmlrpc php-soapReload Apache or NGINX to apply the changes.
sudo systemctl restart apache2sudo systemctl restart nginx
Downloading WordPress for Ubuntu 22.04
The Ubuntu LAMP or LEMP stack is now fully configured and ready for WordPress. Follow these steps to download and install WordPress.
Create a new
srcdirectory inside the root directory for the website. The root directory is normally located atvar/www/html/. Replaceexample.comwith the name of the domain.sudo mkdir -p /var/www/html/example.com/srcEnter the new directory.
cd /var/www/html/example.com/srcDownload the WordPress package using
wget.sudo wget http://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gzExtract the WordPress files from the
tarfile.sudo tar -xvf latest.tar.gz(Optional) Rename the archive using the current date. This makes it easier to restore the files in the future.
sudo mv latest.tar.gz wordpress-`date "+%Y-%m-%d"`.tar.gzMove the extracted files to the root directory for the domain. In a typical configuration, this is the
public_htmldirectory.sudo mv wordpress/* ../public_html/Ensure the webserver user is given ownership over the entire root directory for the domain.
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/example.com
Configuring WordPress on Ubuntu 22.04
Visit the domain using a web browser. The default language selection page first appears. Choose your language and select Continue.
http://example.com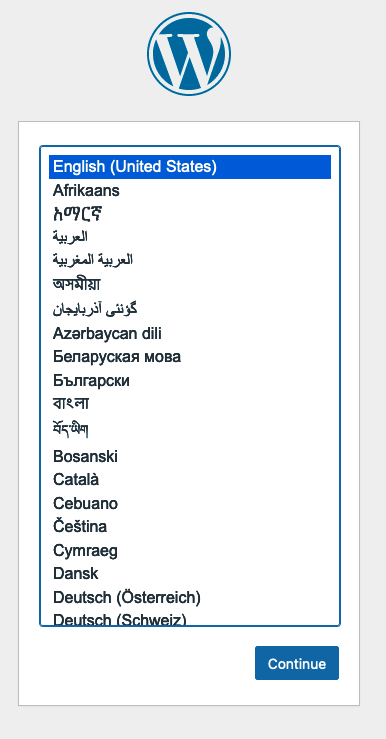
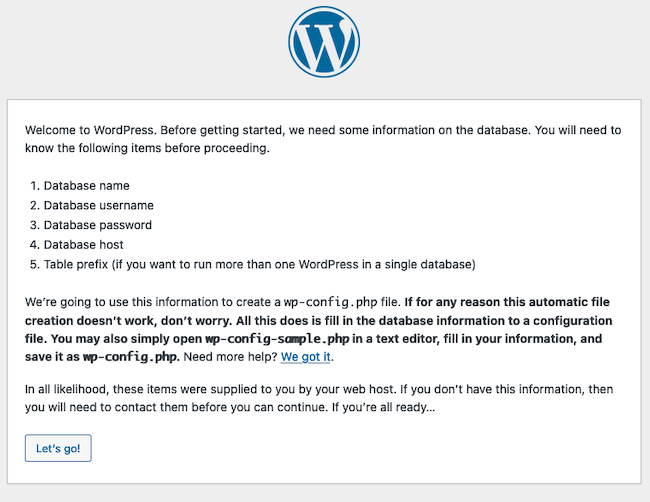
WordPress then displays an informational page explaining the configuration process and required information. Have the database and user details readily available. Click the Let’s Go button to continue.
On the next form, enter the name, user name, password, and host for the database. Use
localhostfor theDatabase Hostfield. If this is the first WordPress installation on the Ubuntu server, leave theTable Prefixfield set towp_. Click the Submit button after entering all the information.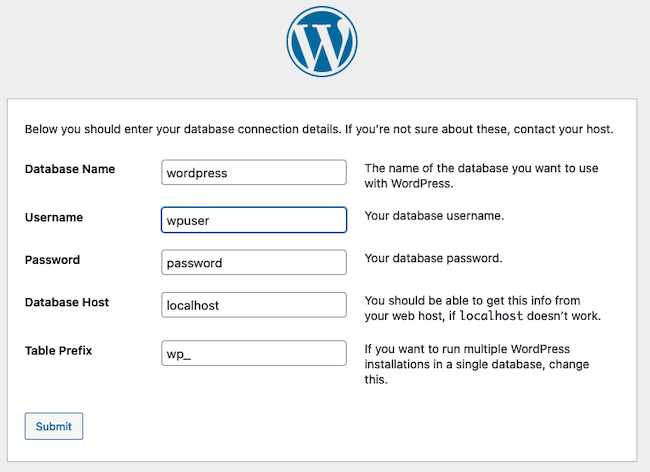
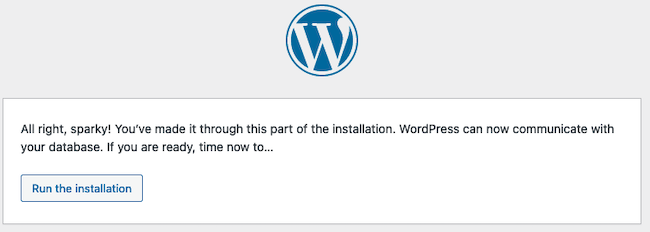
If the information is correct, WordPress confirms the database connection is successful. If there is a connection error, WordPress prompts you to correct the errors. Most failures are due to an incorrect user name or password. Click the Run the installation button to continue.
The next form prompts for a username, password, and email for the site administrator. It also prompts for a site name and asks whether search engines should index the site. Enter all information and then select Install WordPress to continue.
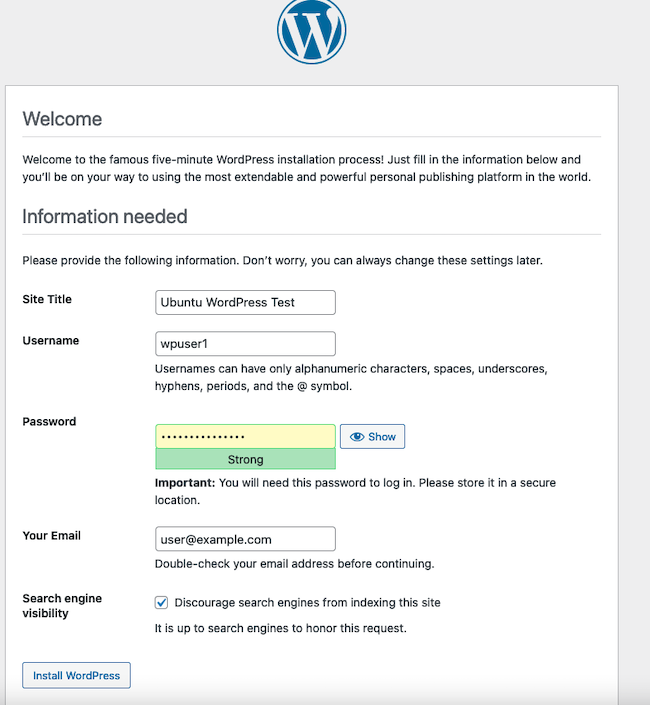
WordPress confirms the account has been successfully created. Click the Log In button to continue to the login screen.
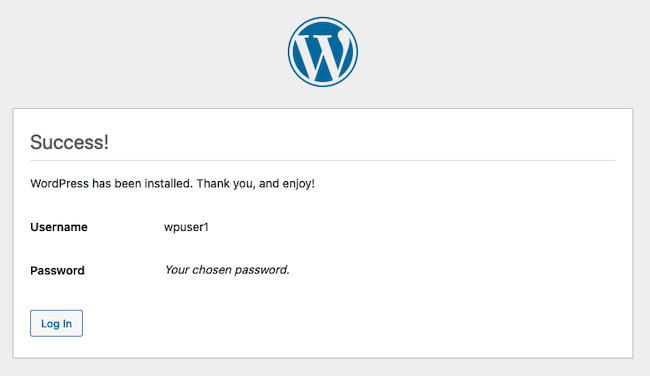
At the login page, enter the user name and password for the WordPress account and click Log In.
The browser displays the WordPress dashboard. Use the dashboard to configure and administer the site, or to add new content. Bookmark the dashboard for future reference. You can also visit it by appending
/wp-adminto the domain name, for examplehttp://www.example.com/wp-admin/.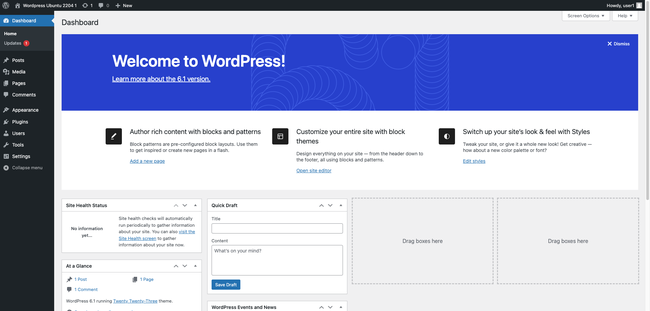
(Optional) WordPress typically uses FTP credentials to install new themes and plug-ins. Add the following lines to the
wp_config.phpfile to remove this restriction. This file is located in the root directory for the domain inside thepublic_htmlsubdirectory.- File: /var/www/html/example.com/public_html/wp-config.php
1 2/** Bypass FTP */ define('FS_METHOD', 'direct');
At this point, the WordPress site is ready to use. To see how the site appears to other users, enter the name of the domain in the address bar of the browser. While logged in, you can also add new content directly from this page.

Learning More about WordPress
The WordPress Dashboard is fairly self-explanatory. From the left-menu of the Dashboard, users can access pages allowing them to change settings, select themes, and install new plug-ins. Users can select the Posts option to add new pages or modify existing content.
Before proceeding, it is worthwhile to spend more time learning about WordPress. The First Steps with WordPress guide is very useful. It walks users through the WordPress interface and explains how to perform basic tasks. In addition, How to Configure WordPress summarizes how to configure some of the more common WordPress settings.
For complete information about WordPress, including all advanced settings, see the WordPress documentation site.
A Summary about Installing WordPress on Ubuntu 22.04
WordPress is one of the most popular CMS applications for personal websites and blogs. It allows site owners to easily manage and customize their sites and quickly add new content. No knowledge of HTML, CSS, or PHP is required.
It is easy to install WordPress on Ubuntu. WordPress requires a Ubuntu LAMP or LEMP stack, including a web server, RDBMS, and the PHP programming language. Download the WordPress files using wget and unzip the archive. A few further adjustments to the LAMP/LEMP stack are also required. After installation, set up WordPress using its intuitive web interface. For more information on WordPress, see the WordPress website.
More Information
You may wish to consult the following resources for additional information on this topic. While these are provided in the hope that they will be useful, please note that we cannot vouch for the accuracy or timeliness of externally hosted materials.
This page was originally published on
